Name
Salpida
salps, sea grape
Framing
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Tunicata
Class: Thaliacea
Order: Salpida
Habitat
Aquatic, marine. Pelagic.
Feeding
Filter feeders. Feeds on phytoplankton filtered from the water.
Distribution
Distributed throughout the equatorial, temperate and cold oceans and seas. The highest concentrations of salpids are in the Southern Ocean.
Conservation status
No species of the genus is listed as threatened.
Additional information
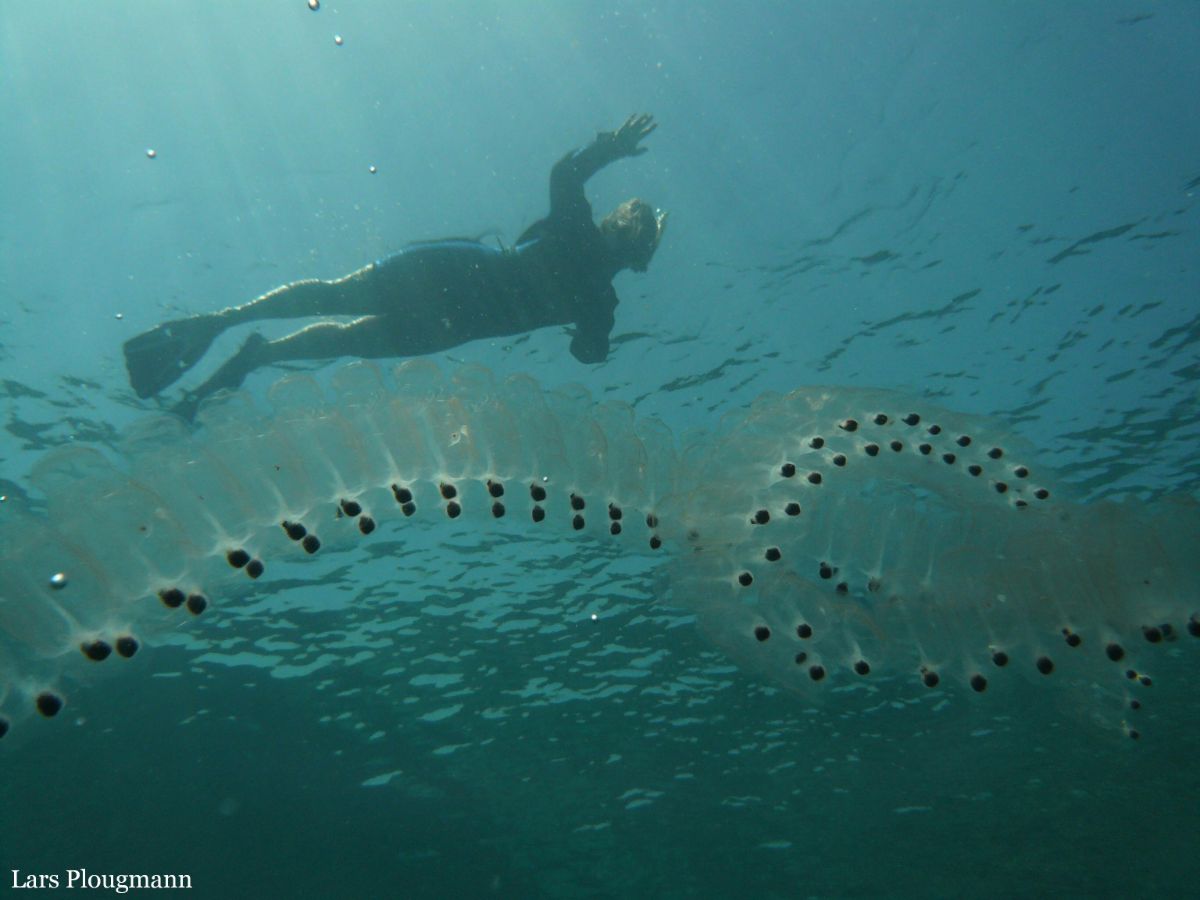
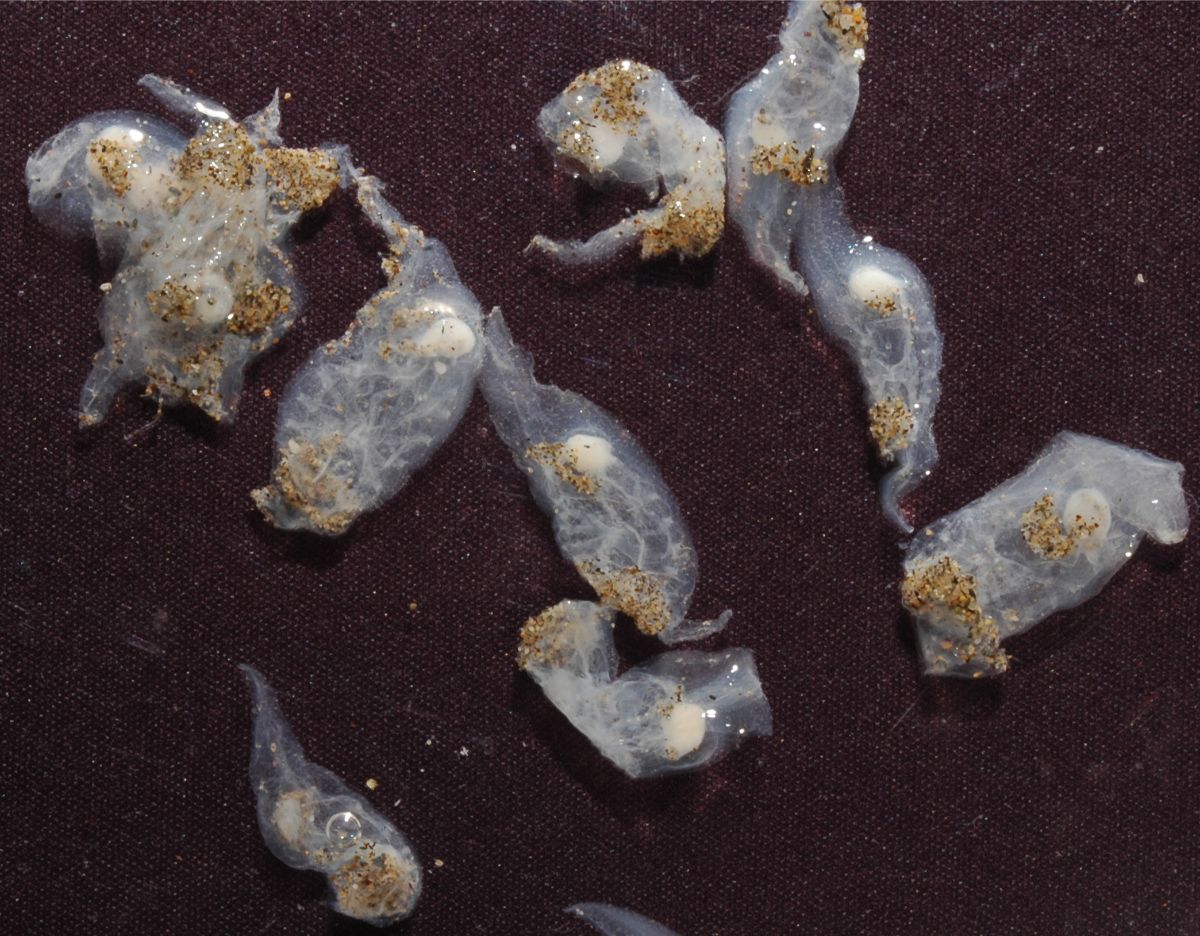
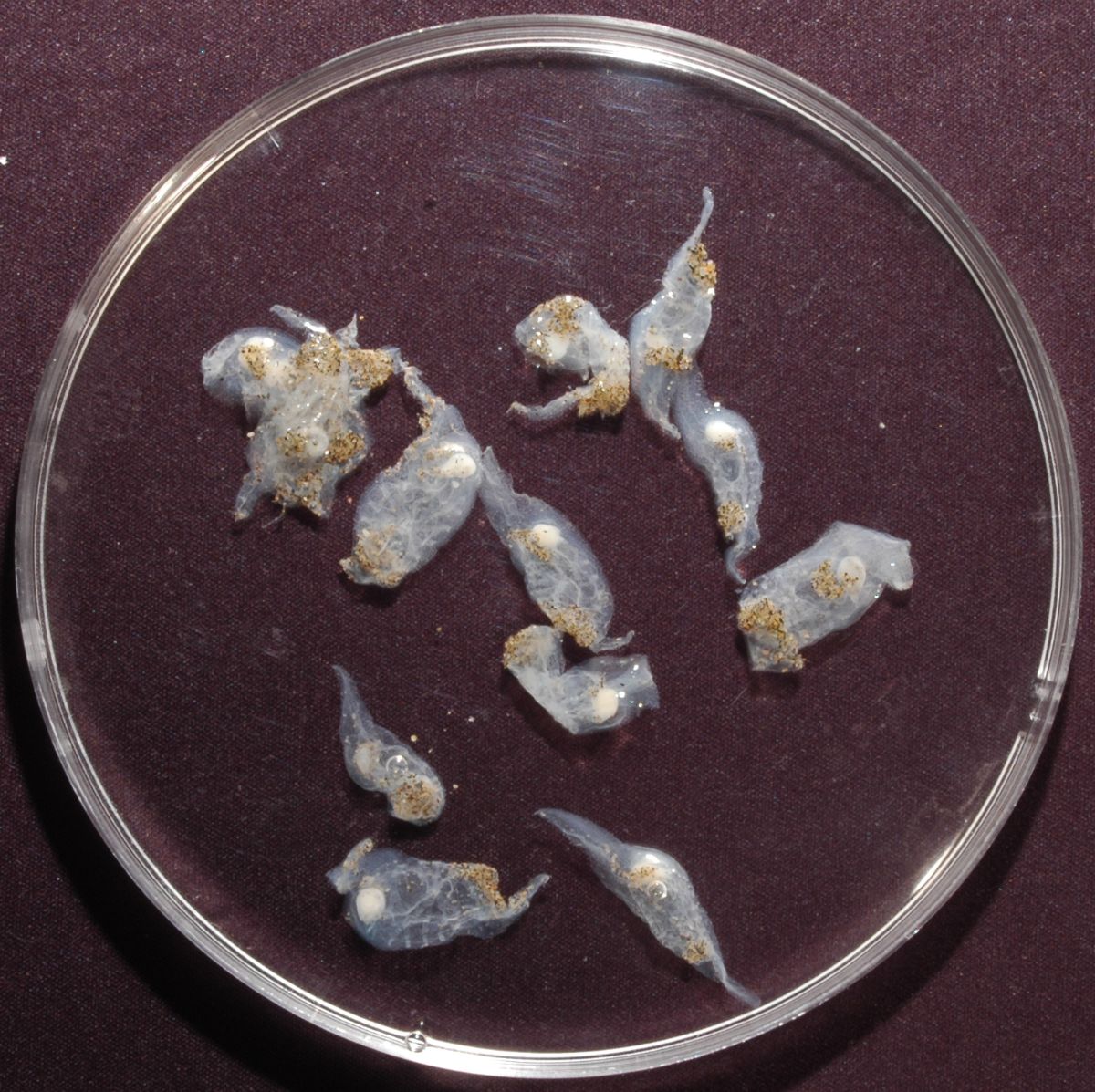
Free. Solitary or colonial. Zooids several cm long with oppositely arranged siphons and muscular bands around the body whose contractions create water currents through the body that enable feeding and locomotion. The muscular bands are visible because the body wall is transparent. By asexual reproduction, they form polymorphic colonies (several types of zooids) in the form of chains that can be more than a metre long.
Additional information
Bibliography
- Brusca, R.C. & Brusca, G.J. (2003). Invertebrates. 2nd edition. Sianauer Associates, Inc., Publishers, Sunderlands, Massachusetts.
- Calvin Calvo, J.C. (1995). El Ecosistema marino Mediterráneo. Guía de su flora y fauna. Omega. Barcelona.
- Gallego, L. 2006. Los Cordados, origen y diversificación. Editorial Club Universitario.
- Madin, L. (2018). World List of Thaliacea. Salpa fusiformis Cuvier, 1804. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=137272 on 2018-03-23
- Madin, L. (2018). World List of Thaliacea. Salpa maxima Forskål, 1775. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=137273 on 2018-03-22
- Riedl, R. (1986). Fauna y flora del mar Mediterráneo. Omega. Barcelona. 858 pp.